Importance of STP plants in today's residential and commercial buildings
Importance of STP plants in today’s residential and commercial buildings
19th May 2022

Food, shelter and water are essential for human survival. However, with the population explosion, demand for the resources have become difficult. Saving these resources is a priority.
As water is vital to Kidneys, likewise, sewage treatment plants are to the city.
Based on a recent worldwide survey, 2 out of 10 people do not have access to clean drinking water. But, why?
The water that flows into the rivers, ponds, and other natural resources is polluted with domestic waste, sewage, and industrialization.
Thereby, it’s important to follow the 5 R’S (Reduce, Recycle, Reuse, Refuse, and Recover) in our daily lives to make sure potable water is available for people around us.
When we talk about Reuse-STP (Sewage treatment plant) is the most prominent solution. It helps to remove toxins, pollutants, and contaminants from the sewage water and produces clean water.
The sewage treatment has 3 main processes –
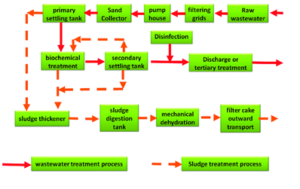
OUTPUT:
The main by-products from the STP are water, sludge, and biogas:
Water: The treated water enters natural resources / reused.
Sludge: It is treated in another treatment plant and used as manure.
Biogas: This helps in meeting its 75%-80% energy requirement for operation and maintenance.
By meeting the water demand, it is important not to throw sewage directly into natural resources. This treated water in turn reduces the overall demand for freshwater.
The continuous increase in scarcity of fresh water and environmental concerns, drives in wastewater reuse. With the advent of green building rating systems; sewage treatment plants should be made mandatory for certification of a structure.
By doing so, this rises the number of STPs and decreases the use of fresh water.
The main focus of setting up mandatory STPs in buildings is that, if each one of us cleaned our own mess instead of dumping it in rivers and lakes, we would have an uninterrupted clean water, which is fit for human consumption flowing straight out of the tap, like developed countries such as Denmark, Singapore, New Zealand, Finland etc.
For example, in Singapore, tap water is thoroughly compliant with the WHO guidelines, as drinking water quality, so much so clean, that there is no need for further filtration or boiling the tap water.
Based on total dissolved solids (TDS) the water can be categorized for using different purposes:
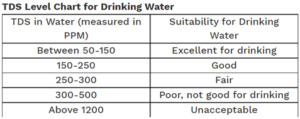
In housing societies, the treated water can be used for non-potable purposes like gardening, washing cars, construction, and flushing the toilet etc
Installation of water-efficient fixtures, swiftly improves the septic tank operation, by actively minimizing wastewater generation.
By adapting measures like high-efficiency toilets, cloth washers, dishwashers, showerheads, and faucet aerators can improve indoor water usage.
Following the above water-efficient measures can reduce the amount of wastewater treatment, which is directly proportional to the reduction in the capacity of STP cost, and environmentally efficient.
RECOMMENDED

Welcome to the captivating realm of symbiotic farms, where nature's harmony and sustainable practices intertwine....

In India's pursuit of a greener future, the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) has established rigorous standards for sustainable buildings. ...

Chennai, a vibrant coastal city in India, has been grappling with recurring flood events during cyclonic storms. ...